Business Software: Tools for Operations and Management
Modern businesses rely heavily on specialized software solutions to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and maintain competitive advantage. From customer relationship management to project coordination, the right digital tools can transform how organizations function. Understanding the various categories of business software and their applications helps companies make informed decisions about technology investments that support growth and efficiency.
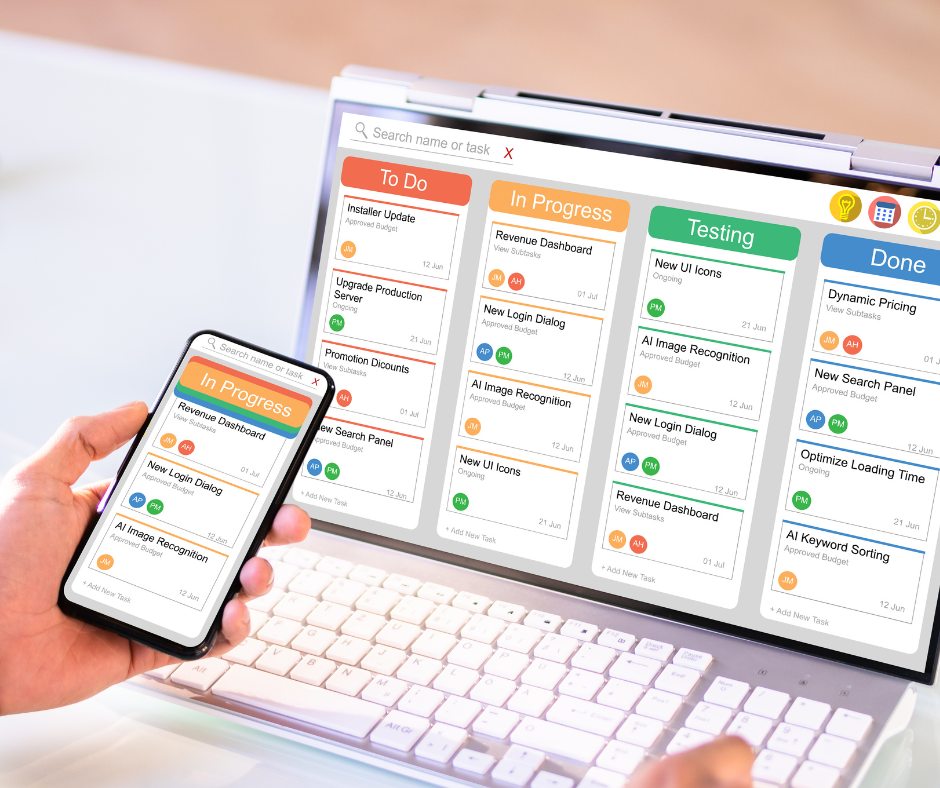
Understanding Business Productivity Tools
Business productivity tools encompass a wide range of software applications designed to help organizations accomplish tasks more efficiently. These tools typically include document management systems, communication platforms, scheduling applications, and collaboration software. Popular productivity suites like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace provide integrated environments where teams can create, share, and manage documents while maintaining seamless communication.
The effectiveness of productivity tools often depends on how well they integrate with existing workflows. Many organizations benefit from cloud-based solutions that allow remote access and real-time collaboration. Features such as version control, automated backups, and cross-platform compatibility have become essential considerations when selecting productivity software.
Exploring Operational Software Solutions
Operational software solutions focus on managing core business processes such as inventory management, customer service, financial tracking, and human resources. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems like SAP and Oracle provide comprehensive platforms that integrate multiple operational functions into unified systems.
These solutions typically offer modules for different departments, allowing businesses to customize their software environment based on specific needs. Manufacturing companies might prioritize inventory and supply chain modules, while service-based businesses may focus on customer relationship management and billing capabilities. The scalability of operational software ensures that solutions can grow alongside business expansion.
Implementing Digital Workflow Systems
Digital workflow systems automate and optimize business processes by creating structured sequences of tasks and approvals. These systems reduce manual intervention, minimize errors, and provide transparency throughout various operational procedures. Workflow automation tools like Zapier, Microsoft Power Automate, and custom-built solutions help organizations eliminate repetitive tasks.
Effective workflow systems include features such as task assignment, progress tracking, automated notifications, and reporting capabilities. They often integrate with existing software applications to create seamless data flow between different business tools. The implementation of digital workflows typically results in improved efficiency, reduced processing times, and better compliance with organizational standards.
Comparison of Leading Technology Providers
| Provider | Software Type | Key Features | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | Productivity Suite | Office apps, cloud storage, collaboration | $6-22 per user/month |
| Salesforce | CRM Platform | Customer management, sales automation | $25-300 per user/month |
| SAP | ERP System | Enterprise resource planning, analytics | $150-300 per user/month |
| Slack | Communication Tool | Team messaging, file sharing, integrations | $7.25-15 per user/month |
| Asana | Project Management | Task tracking, team collaboration, reporting | $10.99-24.99 per user/month |
| QuickBooks | Accounting Software | Financial management, invoicing, payroll | $15-200 per month |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Selecting the Right Software for Your Organization
Choosing appropriate business software requires careful evaluation of organizational needs, budget constraints, and technical requirements. Companies should assess their current processes, identify areas for improvement, and determine which software categories would provide the most significant impact. Factors such as user adoption, training requirements, and integration capabilities play crucial roles in successful software implementation.
Many organizations benefit from conducting pilot programs or utilizing free trial periods to evaluate software performance before making long-term commitments. It’s also important to consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, training expenses, and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Future Trends in Technology Solutions
The software landscape continues evolving with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics. These innovations are being integrated into traditional applications to provide predictive insights, automated decision-making, and enhanced user experiences.
Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly dominant, offering improved accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises installations. Mobile compatibility and remote work capabilities have also become essential features as organizations adapt to changing work environments and employee expectations.
Technology solutions serve as the foundation for modern organizational operations, enabling companies to optimize processes, improve collaboration, and maintain competitive advantages in rapidly changing markets. The strategic selection and implementation of appropriate tools can significantly impact organizational success and long-term sustainability.




